PLATINUM GROUP METALS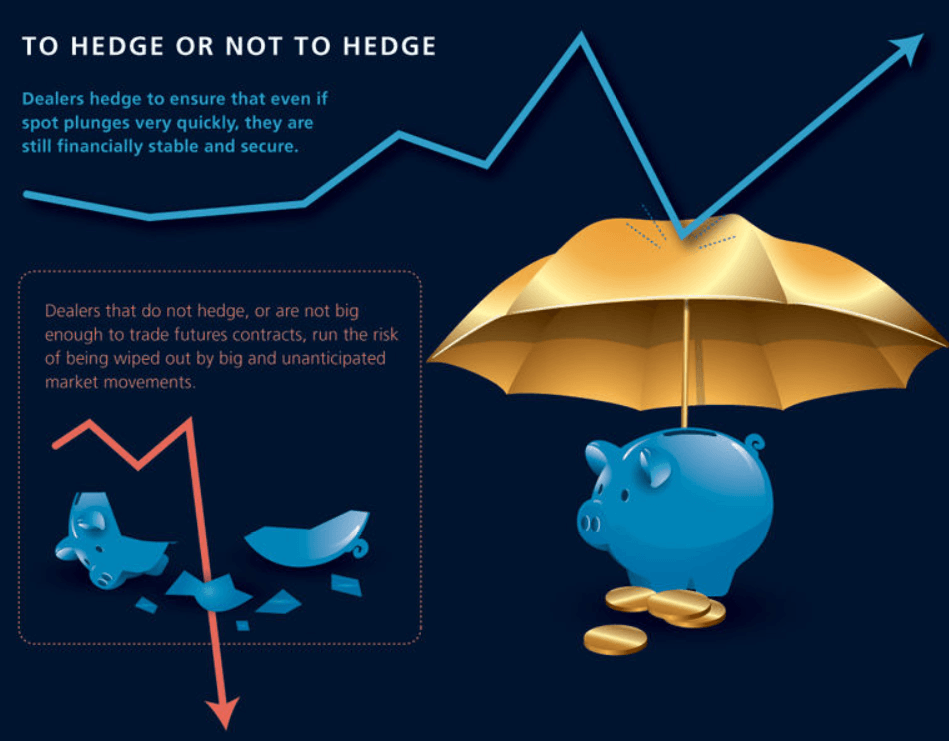
We are committed to honoring all our transactions and therefore we employ a risk management strategy known as “hedging” in order to minimize the possibility of financial loss from fluctuations in commodity prices.
Having ascertained the precious metal content of your scrap catalytic converters, the transformed value is sold on the market at the current price based on an agreed delivery date.
As well, we can provide secure physical precious metal storage for those wishing to hold stock in expectation of better prices at a later date.
To hedge or not to hedge ?
Dealers hedge to ensure that even if spot plunges very quickly, they are still financially stable and secure.
Dealers that do not hedge, or not big enough to trade futures contracts, run the risk of being wiped out by big and unanticipated market movements.
Pt78PLATINUM
A silver-white metal and one of the heaviest substances known to man, is value is in its rarity, its “preciousness” in its special characteristics; it can be shaped and worked in almost any way – only gold and silver are more malleable; it does not corrode nor tarnish, making it a perfect jewelry metal; it has a high melting point; it readily forms alloys with other metals. It also acts extremely effectively as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions, and is, therefore, ideal for automobile catalytic converters.

Pd45PALLADIUM
Palladium is a lustrous silver-white metal and falls within the platinum metals group in the chemical elements periodic table. Palladium possesses several remarkable properties that make it crucial to a number of important applications. Its most significant is its ability to absorb 900 times its own volume of hydrogen, making it the most effcient and safest medium for storing and purifying the gas. It is also an excellent oxidation catalyst, is conductive, resistant to oxidation and very ductile when annealed. These qualities make Palladium a key component in catalytic converters, because of which demand has risen dramatically over the past decades.

RH46 RHODIUM
The rarest of all non-radioactive substances (and hence the most expensive precious metal), Rhodium is a lustrous, silver-white metal that has the important characteristics of being chemically resistant, insoluble in most acids, other than hot concentrated sulfuric acid, highly resistant to corrosion and has a low and stable contact resistance. Industrially, its prime use is as an alloying agent to harden its partner “noble” metals, Platinum and Palladium, but its rarity means that there is, increasingly, very little available naturally; recycling is critical to its continued presence, and use, in catalytic converters.


























